Poor oral care can lead to serious health issues, including infections and chronic inflammation.
Introduction
Did you know that poor dental health is linked to a 24% increased risk of heart disease, according to a 2018 study in the Journal of the American Heart Association? Dental health is often overlooked as a minor aspect of well-being, but it plays a critical role in overall health, impacting everything from cardiovascular function to mental clarity. This article explores how dental health affects overall health, examining its connections to heart disease, diabetes, mental well-being, pregnancy outcomes, and immune function, while offering practical tips to maintain a healthy mouth for a healthier body.
The Evolution of Dental Health and Its Role in Well-Being
The relationship between dental health and overall health has been recognized for centuries, though modern science has deepened our understanding of this connection. In ancient Egypt, around 3000 BCE, tooth decay was treated with herbal remedies, and early physicians noted that oral infections could lead to systemic illnesses. By the 18th century, the “focal infection theory” emerged, suggesting that bacteria from the mouth could spread to other parts of the body, causing diseases—a theory later validated by microbiology.
The 20th century brought advancements in dental care, such as the widespread use of fluoride and the development of modern dentistry, which highlighted the importance of oral care in preventing broader health issues. Today, the American Dental Association (ADA) emphasizes that dental health is a window to overall health, with poor oral hygiene linked to numerous systemic conditions. Key concepts to understand include the role of the oral microbiome—the community of bacteria in the mouth—and its impact on the body.
A balanced oral microbiome supports dental health, but when harmful bacteria proliferate due to poor oral care, they can cause gum disease, tooth decay, and inflammation that spreads beyond the mouth. Periodontal disease, a severe form of gum disease, is particularly concerning, as it allows bacteria to enter the bloodstream, affecting distant organs. These insights underscore why dental health is so crucial for overall health, setting the stage for a deeper exploration of its effects.
How Does Dental Health Affect Heart Health?
Dental health directly impacts heart health through its connection to cardiovascular disease. Poor oral care, particularly gum disease, can lead to chronic inflammation in the body, which is a known risk factor for heart issues. Bacteria from the mouth can enter the bloodstream, contributing to the buildup of plaque in arteries—a condition called atherosclerosis.
This can increase the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular events. A 2020 study in the European Heart Journal found that individuals with periodontal disease were 28% more likely to develop coronary artery disease compared to those with healthy gums. Additionally, the inflammation caused by gum disease can elevate levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), a marker of inflammation associated with heart disease risk.

Maintaining good dental health through regular brushing, flossing, and dental checkups can help reduce these risks, protecting both your mouth and your heart for better overall health.
Can Dental Health Impact Diabetes Management?
Dental health affects overall health by influencing diabetes management, a critical concern for millions worldwide. People with diabetes are more prone to gum disease due to higher blood sugar levels, which create an environment where harmful bacteria thrive. Conversely, gum disease can make it harder to control blood sugar, creating a vicious cycle that worsens both conditions.
This bidirectional relationship highlights the importance of oral care for those with diabetes. A 2019 study in Diabetes Care found that treating periodontal disease in diabetic patients improved their blood sugar control by reducing HbA1c levels by 0.4%—a significant improvement for long-term health. Poor dental health can also lead to infections that cause systemic inflammation, further complicating diabetes management.
By prioritizing dental health, individuals can better manage diabetes, reducing the risk of complications like kidney disease or neuropathy, and supporting overall well-being.
What’s the Link Between Dental Health and Mental Well-Being?
Dental health affects overall health through its impact on mental well-being, an often-overlooked connection. Poor oral health, such as tooth loss or gum disease, can lead to embarrassment, low self-esteem, and social anxiety, as individuals may feel self-conscious about their appearance or bad breath. Chronic dental pain can also contribute to stress, irritability, and even depression, affecting quality of life.
Research highlights this relationship. A 2021 study in the Journal of Clinical Periodontology found that individuals with severe gum disease were 37% more likely to report symptoms of depression compared to those with healthy gums. Additionally, the discomfort of dental issues can disrupt sleep, further exacerbating mental health challenges.
By maintaining good dental health, we can boost confidence, reduce stress, and support mental well-being, all of which are essential for overall health.
How Does Dental Health Affect Pregnancy Outcomes?
Dental health affects overall health in significant ways during pregnancy, impacting both the mother and the baby. Pregnant women with gum disease are at higher risk for complications like preterm birth and low birth weight, as the inflammation and bacteria from the mouth can travel through the bloodstream to the placenta. Poor oral care can also increase the risk of preeclampsia, a dangerous condition characterized by high blood pressure during pregnancy.
A 2020 study in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology found that pregnant women with untreated periodontal disease were 20% more likely to deliver preterm compared to those with healthy gums. To protect both maternal and fetal health, the ADA recommends maintaining good oral care during pregnancy, including:
- Brushing twice daily with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste.
- Flossing daily to clean between teeth and prevent gum inflammation.
- Scheduling a dental checkup during the second trimester, when procedures are safest.
- Eating a balanced diet and limiting sugary snacks to reduce cavity risk.
By prioritizing dental health, expectant mothers can reduce pregnancy risks, ensuring a healthier start for their babies and supporting their own well-being.
Why Is Dental Health Important for Immune Function?
Dental health affects overall health by influencing the immune system, which plays a critical role in fighting infections and maintaining well-being. Poor oral care can lead to infections like gum disease or tooth abscesses, which tax the immune system as it works to combat the bacteria. If left untreated, these infections can spread to other parts of the body, causing systemic issues like endocarditis (an infection of the heart lining) or sepsis, a life-threatening condition.
For example, bacteria from the mouth can travel to the lungs, increasing the risk of respiratory infections like pneumonia, especially in older adults or those with compromised immune systems. A 2019 study in the Journal of Dental Research found that individuals with poor dental health were 15% more likely to develop respiratory infections compared to those with good oral hygiene. Maintaining dental health through regular oral care practices helps reduce the burden on the immune system, allowing it to focus on other threats.
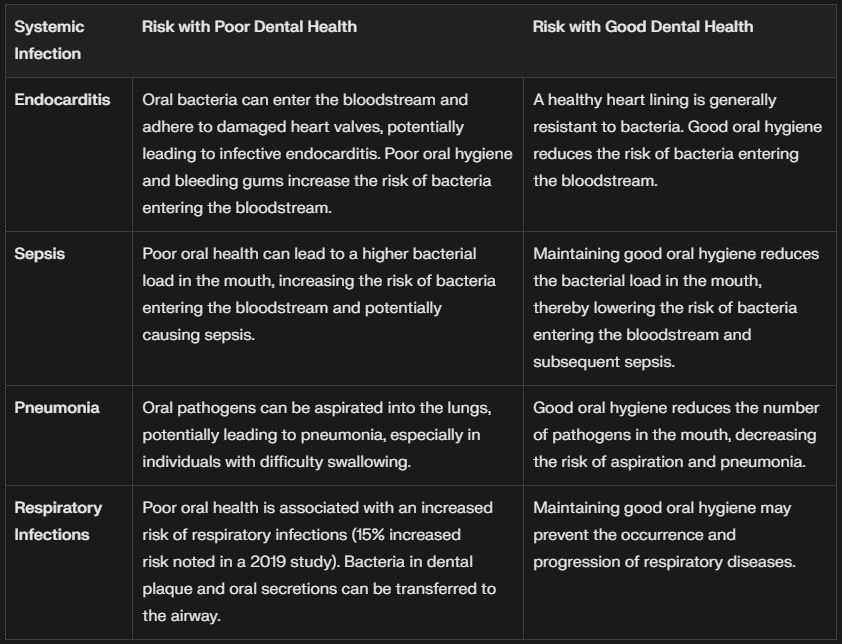
This supports overall health and prevents systemic complications.
How Does Dental Health Influence Digestion?
Dental health affects overall health by playing a key role in digestion, the process that fuels our body with nutrients. Healthy teeth are essential for chewing food properly, which is the first step in digestion. Poor dental health, such as missing teeth or painful gums, can make chewing difficult, leading to improper digestion and nutrient absorption.
This can result in gastrointestinal issues like acid reflux or malnutrition, particularly in older adults. For instance, individuals with tooth loss may avoid hard-to-chew foods like fruits and vegetables, missing out on essential vitamins and fiber. A 2022 study in the Journal of Nutrition found that older adults with poor dental health had a 10% higher risk of malnutrition compared to those with healthy teeth.
By keeping our teeth and gums in good condition, we ensure that digestion starts off right, supporting overall health and well-being through proper nutrition.
Practical Tips for Maintaining Dental Health
Given the many ways dental health affects overall health, adopting good oral care habits is essential. Here are some practical strategies to keep your mouth healthy:
- Brush twice a day with fluoride toothpaste for at least two minutes each time.
- Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between teeth.
- Consider using an antimicrobial mouthwash to kill harmful bacteria.
- Schedule dental checkups and cleanings every six months to catch issues early.
- Limit sugary foods and drinks, such as candies, sodas, and sticky snacks, which can lead to cavities.
- Drink plenty of water to keep your mouth moist and wash away food particles.
- If you smoke, seek support to quit, as smoking increases the risk of gum disease and oral cancer.
These strategies can help you maintain dental health, reducing the risk of systemic health issues and enhancing your overall well-being.
Overcoming Barriers to Dental Care
Many people face barriers to maintaining dental health, such as cost, fear of the dentist, or lack of access to care. To overcome these, look for affordable dental clinics or payment plans, and communicate your fears with your dentist—many offer sedation options to ease anxiety. If access is an issue, focus on at-home oral care practices like brushing and flossing, and use community resources like free dental screenings.
Addressing these barriers ensures that dental health remains a priority. This, in turn, supports your overall health over the long term. Taking proactive steps can make a significant difference in preventing dental issues from impacting your well-being.
Dental Health as a Gateway to Total Well-Being
Dental health affects overall health in profound ways, from reducing the risk of heart disease and improving diabetes management to supporting mental well-being, pregnancy outcomes, immune function, and digestion. A healthy mouth is a gateway to a healthier body, enhancing every aspect of our life. By prioritizing oral care, you can protect your overall health and enjoy a higher quality of life.
Additionally, dietary supplements like calcium or vitamin D can support dental health by strengthening teeth and gums, complementing your oral care routine. Take the first step toward better health by scheduling a dental checkup today.
* Consult your healthcare professional before using any dietary supplements.