A balanced approach to supplementation can enhance your skincare routine for a radiant complexion.
Introduction
Have you ever wondered if a daily supplement could give you that coveted glowing complexion? The question “Can supplements improve your skin?” has gained traction as more people seek internal solutions for skin health, with the global beauty supplement market projected to reach $7 billion by 2024. This article dives into the scientific truth behind supplements for skin health, exploring their benefits, limitations, and practical ways to incorporate them into your routine for a healthier, more vibrant complexion.
The Science of Skin Health and Nutrition
Skin health is deeply tied to nutrition, as the skin relies on vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients to maintain its structure, repair damage, and protect against environmental stressors. The outermost layer, the epidermis, acts as a barrier, while the dermis provides collagen and elastin for firmness and elasticity. A 2020 review in Nutrients highlighted that deficiencies in key nutrients like vitamin C, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids can lead to dryness, delayed wound healing, and increased inflammation, all of which impact skin appearance.
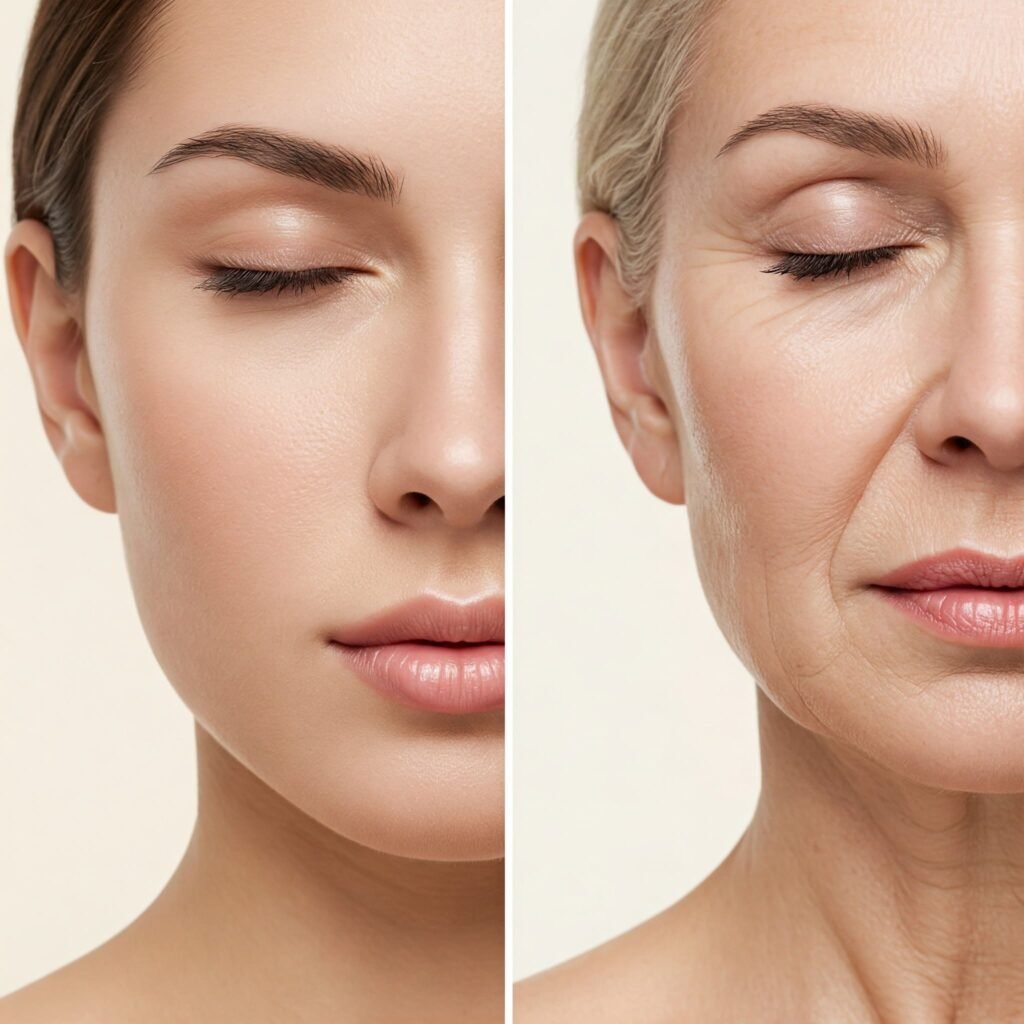
Aging, stress, and poor diet can deplete these nutrients, making supplementation an appealing option. For instance, the body’s natural collagen production drops by about 1% per year after age 20, contributing to wrinkles and sagging. Supplements aim to bridge these gaps, but their effectiveness depends on the nutrient, dosage, and individual factors like absorption and baseline health.
Can Collagen Supplements Reduce Wrinkles and Improve Elasticity?
Collagen supplements, often in the form of hydrolyzed collagen peptides, are among the most popular for skin health. They work by providing the building blocks for collagen synthesis, which supports skin structure and elasticity. A 2019 meta-analysis in the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology found that collagen supplementation (2.5–10 grams daily) improved skin elasticity by 7% and reduced wrinkle depth by 20% after 8–12 weeks in women aged 35–55.
The benefits stem from collagen’s ability to stimulate fibroblasts, the cells that produce collagen and elastin in the dermis. Some studies also report increased skin hydration, as collagen peptides may enhance the skin’s ability to retain moisture. However, results vary—those with severe collagen loss due to advanced aging or sun damage may see less dramatic improvements.
Collagen supplements are generally safe, with few side effects, but they’re not a quick fix. Consistency is key, and combining them with topical treatments like retinoids can enhance results.
Does Vitamin C Support Skin Brightness and Repair?
Vitamin C is a powerhouse for skin health, known for its antioxidant properties and role in collagen synthesis. As an oral supplement, it neutralizes free radicals caused by UV exposure and pollution, which can lead to dullness and premature aging. A 2021 study in Dermatologic Therapy found that 500 mg of daily vitamin C supplementation for 12 weeks increased skin brightness by 15% and reduced hyperpigmentation in participants with uneven skin tone.
Vitamin C also supports wound healing by aiding collagen formation, making it beneficial for repairing sun damage or acne scars. However, its effectiveness as a supplement depends on absorption—high doses (above 2,000 mg daily) may cause digestive upset without additional skin benefits. Pairing vitamin C supplements with a topical serum can maximize its brightening effects, as topical application delivers higher concentrations directly to the skin.
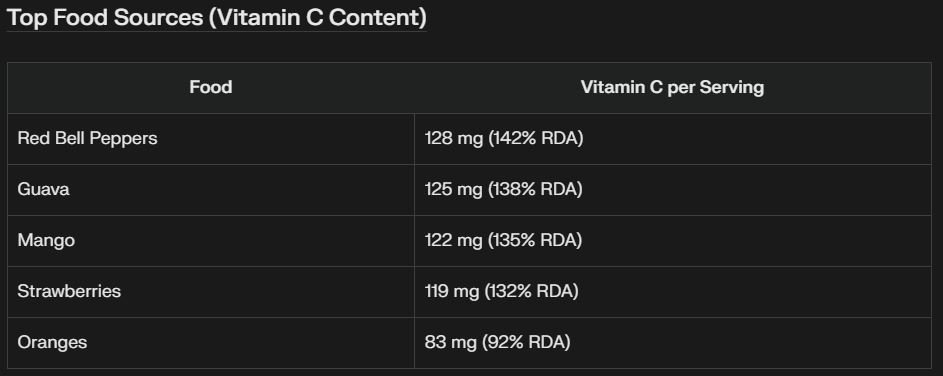
For best results, aim for 500–1,000 mg of vitamin C daily through supplements or foods like oranges and bell peppers. Timing matters—taking it with a meal can improve absorption.
Can Omega-3 Fatty Acids Improve Skin Hydration and Reduce Inflammation?
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oil and algae supplements, are essential fats that support the skin’s lipid barrier, which locks in moisture and protects against irritants. A 2022 study in The Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology found that 1 gram of omega-3 supplementation daily for 12 weeks increased skin hydration by 39% and reduced transepidermal water loss in participants with dry skin. Omega-3s also have anti-inflammatory properties, helping to calm conditions like acne and eczema.
The benefits are linked to omega-3s’ ability to regulate oil production and reduce pro-inflammatory cytokines, which can exacerbate redness and irritation. They may also protect against UV-induced damage, with one study showing a 25% reduction in sunburn sensitivity after three months of supplementation. However, omega-3s can thin the blood, so those on blood thinners should use caution.
A daily dose of 1–2 grams of omega-3s, with a focus on EPA and DHA, can support skin hydration and reduce inflammation. If you don’t eat fatty fish like salmon regularly, supplements are a convenient alternative.
What About Biotin for Skin, Hair, and Nails?
Biotin, a B vitamin (B7), is often marketed for improving skin, hair, and nails, but its benefits for skin health are less clear than commonly believed. Biotin supports the production of fatty acids in the skin, which can enhance the barrier function and reduce dryness. A 2018 study in Dermatology Practical & Conceptual found that 2.5 mg of biotin daily for 12 weeks improved skin smoothness in participants with brittle nails, but the effect on skin alone was minimal unless a deficiency was present.
True biotin deficiency is rare, as it’s found in foods like eggs, nuts, and whole grains, and the body requires only about 30 mcg daily. Excessive doses (e.g., 10,000 mcg in some beauty supplements) can cause acne flare-ups in some people by altering oil production. The hype around biotin may be overstated for those without a deficiency, and research on its direct impact on skin health remains limited.
If you suspect a deficiency—symptoms include thinning hair or scaly skin—biotin supplements may help. Otherwise, focus on a balanced diet to meet your needs.
Can Zinc Supplements Help with Acne and Skin Healing?
Zinc is a mineral with anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties, making it a popular supplement for acne-prone skin. It regulates sebum production and inhibits the growth of Propionibacterium acnes, the bacteria linked to acne. A 2020 meta-analysis in Dermatology found that 30 mg of zinc daily for 12 weeks reduced acne lesions by 28% compared to a placebo, with effects comparable to low-dose antibiotics.
Zinc also supports wound healing by aiding collagen synthesis and immune function, which can help repair acne scars or minor cuts. However, high doses (above 40 mg daily) can cause nausea and interfere with copper absorption, leading to deficiencies over time. Those with sensitive stomachs may benefit from zinc gluconate, which is gentler than zinc sulfate.
Zinc supplements can be a game-changer for acne, but they work best when paired with a consistent skincare routine. Aim for 15–30 mg daily, ideally with a meal to minimize side effects.
Do Antioxidants Like Vitamin E and Selenium Protect Aging Skin?
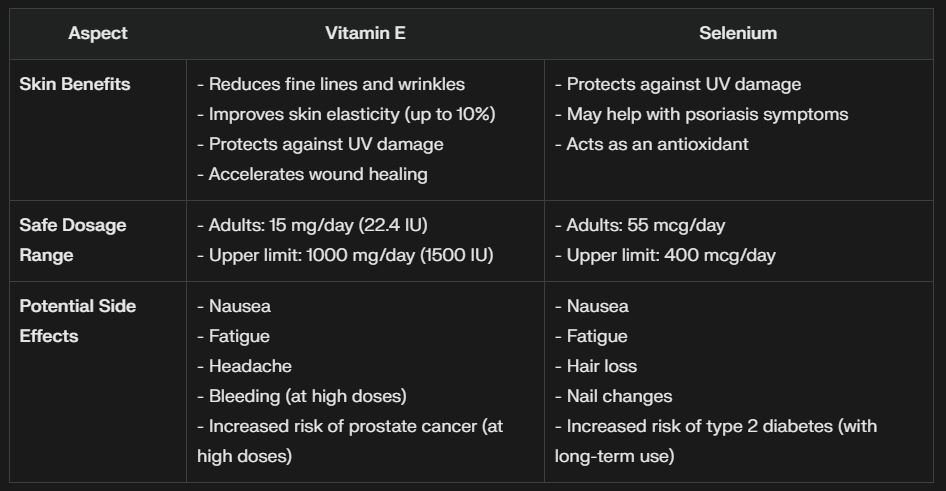
Antioxidants such as vitamin E and selenium protect the skin by neutralizing free radicals, which contribute to aging signs like wrinkles and age spots. Vitamin E, in particular, strengthens the skin’s lipid barrier and reduces UV-induced damage. A 2019 study in Skin Pharmacology and Physiology found that 400 IU of vitamin E daily for eight weeks reduced skin roughness by 12% in participants exposed to high UV levels.
Selenium, often paired with vitamin E, supports the antioxidant enzyme glutathione peroxidase, which protects skin cells from oxidative stress. A 2021 study showed that 200 mcg of selenium daily improved skin elasticity by 10% after 12 weeks, particularly in older adults. However, high doses of selenium (above 400 mcg) can be toxic, causing symptoms like hair loss or gastrointestinal distress.
These antioxidants are most effective for aging skin when combined with a diet rich in fruits and vegetables. Supplements can help, but they’re not a substitute for sun protection.
What Are the Limitations of Supplements for Skin Health?
While supplements can improve skin, they’re not a magic bullet. Their effectiveness depends on factors like absorption, baseline nutrient levels, and the root cause of skin issues. For example, a 2020 review in Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology noted that collagen supplements had little impact on individuals with adequate dietary protein intake, as the body prioritizes essential functions over skin repair.
Some supplements also lack robust evidence—biotin, for instance, shows minimal benefits for skin unless a deficiency exists. Over-supplementation can lead to side effects, such as acne from excessive biotin or digestive issues from high-dose vitamin C. Interestingly, while some believe vitamin C can worsen oiliness, Sodium Ascorbyl Phosphate (SAP), a stable form of vitamin C, actually helps regulate sebum and reduce acne breakouts. Additionally, supplements don’t address external factors like sun damage or poor skincare habits, which play a larger role in skin health.
The placebo effect can also influence perceived benefits, as many studies rely on self-reported improvements. Supplements should be seen as a complement to, not a replacement for, a solid skincare routine and healthy lifestyle.
Practical Tips for Using Supplements to Improve Skin
To maximize the benefits of supplements for skin health, consider these steps:
- Get a blood test to identify deficiencies, such as low vitamin D or zinc, before starting supplements.
- Choose high-quality products with third-party testing to ensure purity and potency.
- Start with one supplement at a time to monitor its effects on your skin, such as collagen for elasticity.
- Pair supplements with a nutrient-rich diet, including foods like berries, nuts, and fatty fish.
- Stay consistent—most supplements take 8–12 weeks to show visible results, so patience is key.
- Use sunscreen daily, as supplements can’t fully protect against UV damage, a major cause of skin aging.
Combining supplements with topical treatments, like a vitamin C serum or hyaluronic acid moisturizer, can enhance their effects. Always prioritize a holistic approach for the best outcomes.
Challenges in Relying on Supplements for Skin Health
Relying on supplements for skin health comes with challenges, including cost, inconsistent results, and misinformation. High-quality supplements can be expensive, and not all products deliver on their promises—some contain fillers or lower doses than advertised. Reading labels and researching brands can help you make informed choices.
Individual responses vary widely due to genetics, diet, and lifestyle. For instance, someone with a balanced diet may see less benefit from biotin than someone with a deficiency. Misleading marketing claims can also create unrealistic expectations, so it’s crucial to focus on evidence-backed supplements like collagen and omega-3s.
Compliance can be an issue, especially if you’re taking multiple supplements daily. Simplify your routine by choosing multi-nutrient formulas or setting reminders to stay consistent.
Supplements as Part of a Broader Skin Health Strategy
Can supplements improve your skin? The scientific truth is yes, but with caveats—they work best when addressing specific deficiencies and are most effective as part of a broader skincare strategy. Collagen can reduce wrinkles, omega-3s can boost hydration, and vitamin C can brighten the complexion, but they’re not a cure-all for skin concerns.
Get Your Doctor’s Approval
Always get your doctor’s approval before beginning any new supplement. Even though they don’t require prescriptions, some supplements may not be safe. Your doctor will ensure there are no potential interactions with your medications or negative side effects.